Ever wonder why some videos play perfectly while others show error messages or look terrible? The answer lies in two behind-the-scenes components working in your computer: decoders and renderers.
Here's how they work together to bring your videos to life.
What Happens When You Click Play
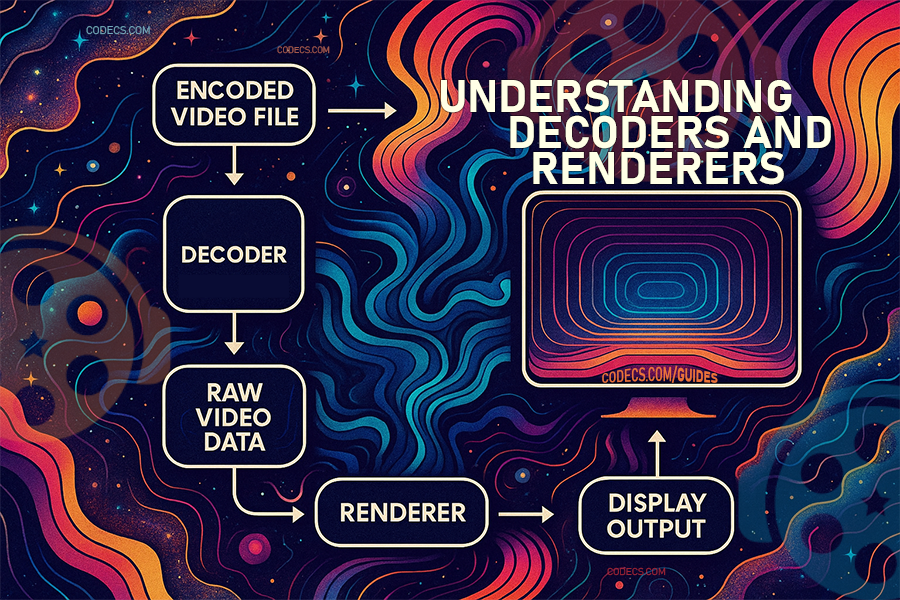
When you double-click a video file, your computer goes through a two-step process that most people never see:
Step 1: A decoder "unpacks" the video file.
Step 2: A renderer displays it on your screen.
Think of it like receiving a compressed package in the mail. The decoder is like unwrapping the package, and the renderer is like arranging the contents so you can actually use them.
What Decoders Actually Do
Video files are like digital suitcases - they're packed tightly to save space.
A 2-hour movie that would normally take up 200GB gets squeezed down to maybe 2GB using compression tricks.
The decoder's job is simple: unpack that compressed video.
Different video formats use different "packing methods":
- MP4 videos are packed one way.
- AVI files use another method.
- MKV files have their own system.
When you get a "codec not found" error, it means your computer doesn't know how to unpack that particular type of video file. It's like receiving a package but not having the right tool to open it.
How Renderers Make Videos Watchable
Once the decoder unpacks your video, you still can't watch it. The unpacked video is just raw data - like having all the pieces of a puzzle dumped out of the box.
The renderer puts everything together for your screen.
Renderers handle the tricky stuff:
- Making sure the video fits your screen properly.
- Keeping the audio synced with the moving pictures.
- Adjusting colors so they look right on your monitor.
- Making everything play smoothly without stuttering.
When Things Go Wrong
Video won't play at all: Usually means you're missing the right decoder. Your computer can't "unpack" that video format.
Video plays but looks awful: Often a renderer problem. The video got unpacked fine, but something went wrong putting it together for display.
Audio doesn't match the video: Classic renderer issue. The decoder did its job, but the renderer isn't keeping sound and picture synchronized.
Colors look weird or washed out: Another renderer problem. It's not translating the colors correctly for your specific monitor.
Real-World Examples
MPC Video Decoder and MPC Video Renderer:
These work as a team specifically for older video formats like DVDs.
The MPC decoder knows how to unpack DVD-style video compression, while the MPC renderer specializes in displaying that content with the right colors and timing.
Why you might need both:
Having just a decoder is like having a can opener but no plate - you can open the can, but you can't properly serve the food.
Having just a renderer is like having a plate but no can opener - useless without the first step.
Making Your Videos Work Better
For most playback problems:
You usually need better decoders that can handle more video formats. Think of it as having a universal tool that can open any type of package.
For quality issues:
Look at upgrading your renderer - the component that actually puts the video on your screen.
The easiest solution:
Many codec packs include both updated decoders and renderers that work well together, like getting a complete toolset instead of individual tools.
Why This Matters to You
Understanding decoders and renderers helps you:
- Know what's actually wrong when videos don't work.
- Make better choices when downloading codec packs.
- Understand why some videos play great on one computer but not another.
- Stop blaming the video file when it's actually a player problem.
Your computer needs both components working together to turn compressed video files into the smooth, colorful, synchronized content you want to watch.
When either component fails or is missing, your video experience suffers.












How to Download HEVC Video Extension for Free
The server returned an empty list. Either you have not entered the link correctly, or this service does not ...
Read More →MPC-BE vs MPC-HC: Which Media Player is Right...
MPC-BE the best for me! Better performance than mpc-hc
Read More →Convert WAV to MP3: Best Quality Settings Gui...
MP3, AAC is only for vintage H/W players. For PC: FLAC. For smarphone: Opus 96~160 kbit/s
Read More →