Ever clicked on a video file only to see an error message? Or downloaded a song that won't play in your music app? You're experiencing the classic codec and file format puzzle that confuses millions of people every day.
What Are Codecs and Why Do They Matter?
Think of codecs as specialized translators for your computer.
When you have a video file, it's compressed using a specific "language" (the codec) to make it smaller.
When you want to play it, your computer needs to understand that same language to decode it.
Common video codecs you'll encounter:
- H.264 - The most popular codec, used in most MP4 files you see online.
- H.265 (HEVC) - Newer codec that creates smaller files with better quality, but requires more computer power.
- VP9 - Google's codec, commonly used on YouTube.
Popular audio codecs:
- MP3 - The classic audio codec everyone knows.
- AAC - Higher quality than MP3, used by Apple and streaming services.
File Formats: The Container That Holds Everything
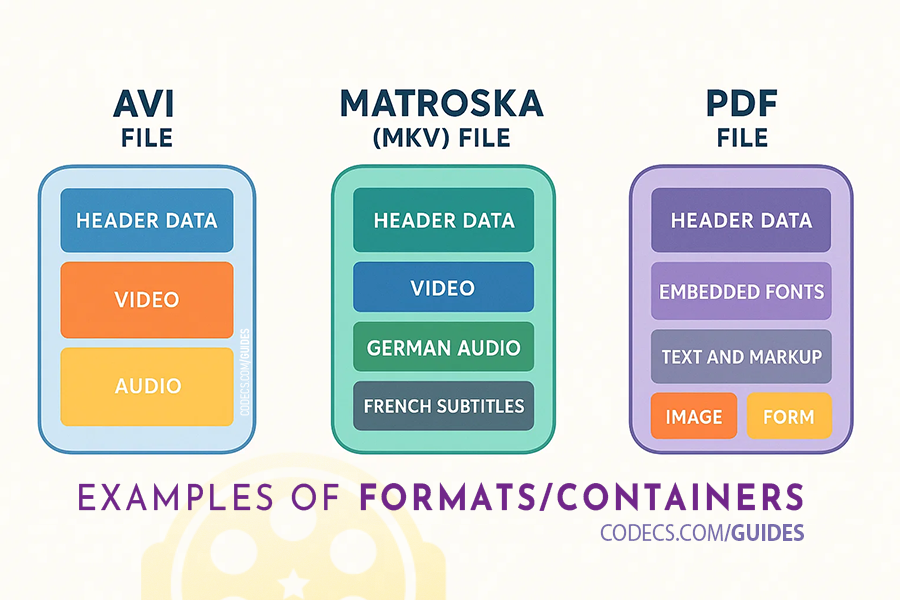
File formats (also called containers) are like boxes that hold your coded content. A single container can hold multiple things - video, audio, subtitles, and more (see the pic below).
Here's what's confusing: An MP4 file might contain H.264 video, but it could also contain H.265 video. Same container, different contents.
That's why some MP4 files play fine while others don't.
Common containers you'll see:
- MP4 - Works almost everywhere, great for sharing.
- AVI - Older format, still widely used.
- WebM - Designed for web browsers.
- WAV - Uncompressed audio, large files but perfect quality.
- PNG: An uncompressed image file format that retains all of the image quality. It's commonly used in graphic design.
Why Files Don't Play (And What's Really Happening)
When your computer says "unsupported format," it usually means one of two things:
- Missing codec - Your computer recognizes the container (.mp4) but can't decode what's inside (H.265 video). → See Common HEVC File Extensions
- Incompatible container - Your player doesn't support that type of file at all.
This is why VLC Player is so popular - it includes dozens of codecs built-in, so it can play almost anything you throw at it.
Choosing the Right Format for Your Needs
For maximum compatibility: Use MP4 containers with H.264 video and AAC audio. This combination works on virtually every device and platform.
For best quality: H.265 creates smaller files with better quality, but not all devices support it yet.
For web use: WebM with VP9 codec loads faster in browsers, while MP4 with H.264 is the universal backup.