Video codecs are the invisible workhorses powering every Netflix binge session, Zoom call, and TikTok scroll. As we move deeper into the 2020s, the codec landscape is undergoing its most dramatic transformation since the transition from standard definition to HD.
With 4K becoming standard, 8K content emerging, and bandwidth still limited in many regions, the efficiency of video compression technology will determine who wins the streaming wars.
The stakes couldn't be higher. Poor codec choices cost streaming platforms millions in bandwidth fees, frustrate viewers with buffering, and limit the quality of content creators can deliver.
Meanwhile, the right codec decisions unlock new possibilities: crystal-clear 8K streams on mobile networks, real-time 4K video calls, and immersive VR experiences that were impossible just years ago.
This comprehensive guide explores exactly where video codec technology is heading, which standards will dominate different markets, and what these changes mean for content creators, streaming platforms, and everyday users.
Why the Codec Revolution Matters More Than Ever
The explosion in video consumption has created a perfect storm demanding better compression.
Consider these numbers: global video streaming traffic increased 400% between 2019 and 2024, 4K content now represents over 35% of premium streaming catalogs, and mobile video consumption accounts for 75% of all internet traffic.
Traditional codecs like H.264, while revolutionary in their time, simply cannot keep pace with this demand.
→ Is AVC/H.264 Making Way for New Video Encoding Stars?
The solution isn't just faster internet - it's smarter compression.
Modern codecs can reduce file sizes by 50-70% compared to H.264 while maintaining identical visual quality. This isn't just technical minutiae; it's the difference between a streaming service being profitable or hemorrhaging money on bandwidth costs.
For content creators, codec choice now directly impacts reach.
A YouTuber using outdated compression might find their 4K uploads unwatchable for viewers on slower connections, while their competitor using AV1 delivers pristine quality to the same audience.
Platform algorithms increasingly favor content that plays smoothly across devices, making codec optimization a competitive advantage.
HEVC (H.265): The Current King's Extended Reign
High-Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC), standardized as H.265 in 2013, currently dominates premium streaming and will continue its reign through at least 2027.
Despite being over a decade old, HEVC's 50% bitrate improvement over H.264 makes it indispensable for 4K and HDR content delivery.
Why HEVC Remains Dominant
HEVC's staying power stems from three key factors: mature hardware support, proven reliability, and extensive platform adoption.
Nearly every smartphone sold since 2018 includes hardware HEVC decoding, while software support spans from Windows Media Player to VLC Player.
Major streaming platforms like Netflix, Amazon Prime, and Disney+ built their 4K infrastructure around HEVC, representing billions in investment that won't be quickly abandoned.
The codec excels particularly in high-resolution content. While H.264 struggles with 4K video, often requiring 25+ Mbps bitrates, HEVC delivers comparable quality at 12-15 Mbps.
For 8K content, HEVC remains the only viable option with widespread hardware support, typically requiring 40-60 Mbps compared to H.264's prohibitive 100+ Mbps.
HEVC's Limitations and Challenges
However, HEVC's dominance comes with significant drawbacks. Patent licensing remains complex and expensive, with multiple patent pools demanding royalties. This has prevented adoption by open-source projects and created uncertainty for smaller companies.
YouTube notably avoids HEVC for this reason, despite its technical superiority.
Encoding complexity is another limitation. HEVC encoding takes 3-5 times longer than H.264, increasing costs for live streaming and user-generated content platforms.
Battery drain during mobile playback also exceeds H.264 by 20-30%, a critical factor for mobile-first platforms.
Real-World HEVC Performance
In practical terms, HEVC shines in professional content distribution but struggles in real-time applications. Netflix reports 45% bandwidth savings using HEVC for its 4K catalog, directly translating to millions in reduced CDN costs.
Conversely, video conferencing platforms like Zoom still rely primarily on H.264 due to HEVC's encoding latency and patent concerns.
Content creators uploading to HEVC-supported platforms see immediate benefits.
A 10-minute 4K video that would consume 2.5GB with H.264 compression drops to 1.2GB with HEVC, halving upload times and storage costs while maintaining identical quality.
AV1: The Royalty-Free Revolutionary
The Alliance for Open Media's AV1 codec represents the most significant threat to HEVC's dominance. Backed by Google, Netflix, Amazon, and other tech giants, AV1 promises HEVC-level compression with zero licensing fees.
AV1's Competitive Advantages
AV1's royalty-free status solves HEVC's biggest weakness. Companies can implement AV1 without patent concerns, making it attractive for open-source projects and cost-conscious developers. Performance-wise, AV1 delivers 20-30% better compression than HEVC, though this varies significantly by content type.
The codec excels with animated content and screen recordings, achieving compression ratios that seemed impossible with previous standards.
YouTube's internal testing shows AV1 reducing animated video file sizes by up to 50% compared to HEVC, while maintaining superior quality.
Browser support has reached critical mass. Chrome, Firefox, and Edge now support AV1 hardware decoding on compatible devices, while Safari added support in 2023. This browser penetration enables direct streaming without additional plugins or apps.
AV1 Adoption Challenges
Despite its advantages, AV1 faces significant adoption hurdles. Hardware support remains limited, with only recent high-end phones and graphics cards including AV1 decoders. Older devices must rely on software decoding, which drains batteries faster and may struggle with higher resolutions.
Encoding speed presents the biggest challenge. AV1 encoding takes 10-20 times longer than H.264, making it impractical for live streaming or real-time applications. While optimized encoders have reduced this gap, AV1 encoding still requires substantially more computational resources than alternatives.
Current AV1 Implementation
Netflix began deploying AV1 for its mobile streams in 2021, reporting 20% bandwidth savings compared to HEVC.
YouTube uses AV1 for many 4K uploads, particularly benefiting creators with animated content.
→ See Enable AV1 Codec on YouTube for Better Video Quality
However, both platforms maintain H.264 and HEVC fallbacks for device compatibility.
The gaming industry shows particular interest in AV1 for streaming and recording applications. NVIDIA's latest graphics cards include AV1 encoders specifically for game streaming, while Xbox Series X supports AV1 playback for streaming apps.
VVC (H.266): The Next-Generation Powerhouse
Versatile Video Coding (VVC), also known as H.266, represents the next evolutionary step in traditional codec development.
Finalized in 2020, VVC promises 50% better compression than HEVC, potentially matching or exceeding AV1's efficiency.
VVC's Technical Superiority
VVC incorporates numerous compression innovations, including improved motion prediction, advanced transform coding, and sophisticated rate control algorithms.
These improvements enable exceptional quality at extremely low bitrates, making 8K streaming viable over current broadband connections.
Initial testing suggests VVC can deliver 4K quality at 6-8 Mbps bitrates, compared to HEVC's 12-15 Mbps requirement. For mobile streaming, this represents a breakthrough enabling high-quality video even on congested cellular networks.
The codec also includes built-in support for emerging technologies like 360-degree video, high dynamic range, and variable refresh rates.
This forward-thinking design positions VVC well for future content formats that current codecs handle poorly.
VVC Adoption Timeline and Barriers
Hardware support remains VVC's primary limitation. Unlike previous codec transitions, VVC's computational complexity requires dedicated silicon, not just software updates.
Industry analysts predict widespread hardware support won't arrive until 2026-2027, limiting near-term adoption.
Patent licensing presents another challenge. While not as complex as HEVC's situation, VVC still carries licensing requirements that may limit adoption by open-source projects and smaller companies.
The patent pool structure remains under development, creating uncertainty for potential implementers.
VVC's Target Applications
Early VVC adoption will likely focus on premium streaming services and professional broadcasting. The codec's exceptional compression makes it ideal for 8K content distribution and high-quality mobile streaming in bandwidth-constrained regions.
Broadcast television particularly benefits from VVC's capabilities.
Several European broadcasters plan VVC transitions for their 4K and 8K services, taking advantage of the codec's ability to deliver cinema-quality video over traditional broadcast channels.
Emerging Codec Technologies and Innovations
Beyond the major standards, several emerging technologies promise to reshape video compression in unexpected ways.
AI-Powered Compression
Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing video encoding through multiple approaches.
Neural network-based codecs like Google's experimental neural video compression achieve unprecedented compression ratios by learning content-specific patterns. While still in development, early results suggest 70% better compression than AV1 for certain content types.
Machine learning also enhances traditional codecs through intelligent preprocessing and encoding optimization.
Netflix's Dynamic Optimizer uses AI to select optimal encoding settings per scene, improving quality while reducing bitrates. This approach works with existing codecs but delivers next-generation performance.
Real-time AI enhancement represents another frontier.
Samsung's latest TVs include AI upscaling that can transform lower-resolution content into near-4K quality, potentially reducing bandwidth requirements by streaming lower resolutions and enhancing them locally.
Cloud-Based Encoding Innovation
Cloud encoding platforms are implementing advanced techniques impossible with traditional hardware encoders.
Per-title encoding, now standard at Netflix and YouTube, analyzes each video individually to optimize compression settings. This personalized approach delivers 20-30% bandwidth savings compared to one-size-fits-all encoding.
Content-aware encoding takes this further, adjusting compression based on scene complexity, motion levels, and visual importance. Action sequences receive higher bitrate allocations, while static scenes use minimal bandwidth, optimizing the viewing experience across diverse content.
Specialized Codec Applications
Gaming content requires different optimization than traditional video. NVIDIA's NVENC encoder includes game-specific presets that prioritize low latency over compression efficiency, essential for streaming and cloud gaming applications.
Screen content codecs address the unique requirements of desktop sharing and remote work. These specialized codecs excel at compressing text, user interfaces, and presentation content, achieving compression ratios impossible with general-purpose video codecs.
Platform-Specific Codec Strategies
Different platforms optimize for varying priorities, leading to diverse codec adoption strategies.
Streaming Platform Approaches
Netflix maintains a multi-codec strategy, using HEVC for 4K content, AV1 for mobile streams, and H.264 for compatibility. This approach maximizes quality while ensuring universal playback, though it increases storage and complexity costs.
YouTube aggressively pushes newer codecs, implementing AV1 for creators while maintaining H.264 fallbacks. Google's platform serves as a testing ground for experimental codecs, leveraging its massive scale to validate new technologies.
Amazon Prime Video focuses on HEVC optimization, particularly for its original content. The platform's extensive HDR catalog benefits from HEVC's superior handling of high dynamic range content, while its global reach necessitates careful bandwidth optimization.
Social Media Platform Considerations
TikTok prioritizes fast encoding and small file sizes over absolute quality, predominantly using optimized H.264 encoding. The platform's short-form vertical video format allows aggressive compression while maintaining acceptable quality.
Instagram balances quality and compatibility, using HEVC for high-quality uploads while generating H.264 versions for broader device support. This dual-encoding approach increases storage costs but ensures optimal experiences across devices.
Live Streaming Platform Requirements
Twitch relies heavily on H.264 for its low latency requirements, though it's testing AV1 for recorded content. Live streaming demands fast encoding, making newer codecs less practical despite their superior compression.
YouTube Live uses adaptive encoding, automatically selecting codecs based on stream complexity and encoder capabilities. High-motion gaming streams use H.264, while slower content may employ HEVC or AV1 encoding.
Impact on Content Creators and Production Workflows
Codec evolution directly affects how content creators work, from shooting decisions to final delivery.
Camera and Recording Considerations
Modern cameras increasingly support HEVC recording, enabling longer recording times and smaller file sizes. However, editing these files requires powerful computers and compatible software, potentially slowing post-production workflows.
Professional cameras are beginning to include AV1 support for specific applications, particularly in documentary and journalism where long recording sessions benefit from superior compression. However, limited editing software support constrains widespread adoption.
Editing and Post-Production Changes
Video editing software adaptation varies significantly. Adobe Premiere Pro supports HEVC and basic AV1 playback, while DaVinci Resolve offers more comprehensive HEVC editing capabilities. Editors increasingly maintain proxy workflows to handle high-efficiency codecs on older hardware.
Color grading and visual effects work particularly benefit from newer codecs' improved chroma handling. HEVC's superior color space support enables more accurate post-production work, while VVC promises even better professional tools support.
Distribution Strategy Evolution
Content creators now require multi-format delivery strategies. A single video might be encoded in H.264 for compatibility, HEVC for quality, and AV1 for efficiency, tripling encoding time and storage requirements but maximizing audience reach.
Platform-specific optimization becomes essential. YouTube creators benefit from AV1 uploads for discoverability, while Instagram creators need HEVC for quality and H.264 for reach. This complexity requires sophisticated content management systems.
Geographic and Market Variations
Codec adoption varies significantly across global markets due to infrastructure differences and regional priorities.
Developed Market Trends
High-bandwidth regions like South Korea and Scandinavian countries rapidly adopt advanced codecs, with 4K streaming becoming standard. These markets drive demand for 8K content and experimental codec testing.
The United States shows mixed adoption, with urban areas embracing 4K streaming while rural regions remain bandwidth-constrained. This divide influences platform codec strategies, with quality tiers based on geographic detection.
Emerging Market Considerations
Bandwidth-limited regions prioritize compression efficiency over absolute quality. AV1's superior compression makes it particularly attractive for mobile-first markets in Southeast Asia and Africa.
Device capabilities also influence adoption. Regions with predominantly older smartphones rely heavily on H.264, while markets with newer devices can leverage HEVC and AV1 benefits.
Regional Platform Preferences
Chinese platforms like Bilibili aggressively implement AV1 due to its royalty-free status and government technology independence preferences. This creates a natural testing ground for AV1 optimization and development.
European platforms balance HEVC adoption with AV1 experimentation, influenced by both technical requirements and regulatory preferences for open standards.
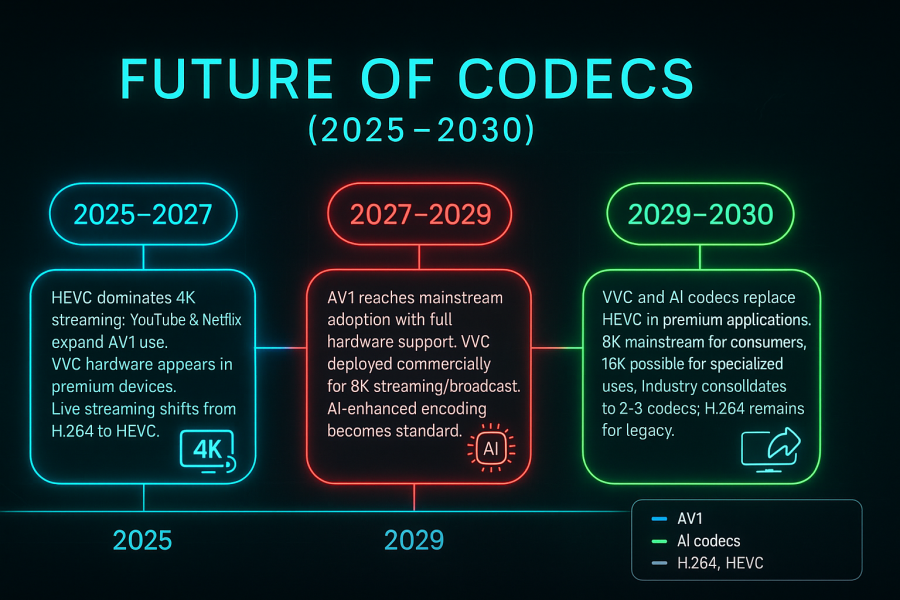
The Road Ahead: Predictions and Timelines
Based on current development trajectories and industry adoption patterns, several trends will shape codec evolution through 2030.
2025-2027: HEVC maintains 4K streaming dominance while YouTube and Netflix expand AV1 for mobile and animated content. VVC hardware appears in premium devices, and live streaming gradually transitions from H.264 to optimized HEVC.
2027-2029: AV1 achieves mainstream adoption as hardware support reaches critical mass, while VVC enters commercial deployment for 8K streaming and broadcasting. AI-enhanced encoding becomes standard across major platforms.
2029-2030: VVC and AI-powered codecs begin replacing HEVC for premium applications, making 8K streaming viable for consumers and 16K content possible for specialized uses. The industry consolidates around 2-3 primary codecs, with H.264 relegated to legacy compatibility.
Practical Recommendations for Different User Types
Content Creators
Immediate actions: Master HEVC encoding for quality-focused platforms while maintaining H.264 compatibility versions. Invest in hardware supporting AV1 encoding for future-proofing. Develop multi-format workflows to optimize for different platforms.
Medium-term strategy: Experiment with AV1 encoding for suitable content types, particularly animation and screen recordings. Prepare for VVC adoption by understanding its technical requirements and benefits.
Streaming Platforms and Services
Current priorities: Implement comprehensive HEVC deployment while testing AV1 for specific use cases. Develop adaptive bitrate streaming with multiple codec support. Invest in per-title encoding and AI optimization.
Future planning: Prepare VVC transition roadmaps aligned with hardware support availability. Consider AI-powered compression solutions for competitive advantage.
Enterprise and Business Users
Immediate needs: Upgrade video conferencing and internal streaming to HEVC where supported. Implement content delivery networks supporting multiple codec formats for global reach.
Strategic considerations: Plan bandwidth budgets assuming gradual codec efficiency improvements. Evaluate AI-powered compression solutions for specific applications like training content and presentations.















MPC-BE vs MPC-HC: Which Media Player is Right...
MPC-BE the best for me! Better performance than mpc-hc
Read More →How to Download HEVC Video Extension for Free
THANKS BRO IT WORKS
Read More →Convert WAV to MP3: Best Quality Settings Gui...
MP3, AAC is only for vintage H/W players. For PC: FLAC. For smarphone: Opus 96~160 kbit/s
Read More →